https://en.sputniknews.africa/20240907/groundbreaking-discovery-zimbabwean-scientists-announce-cure-for-alzheimers-and-melanoma-1068184232.html
Groundbreaking Discovery: Zimbabwean Scientists Announce Cure for Alzheimer's and Melanoma
Groundbreaking Discovery: Zimbabwean Scientists Announce Cure for Alzheimer's and Melanoma
Sputnik Africa
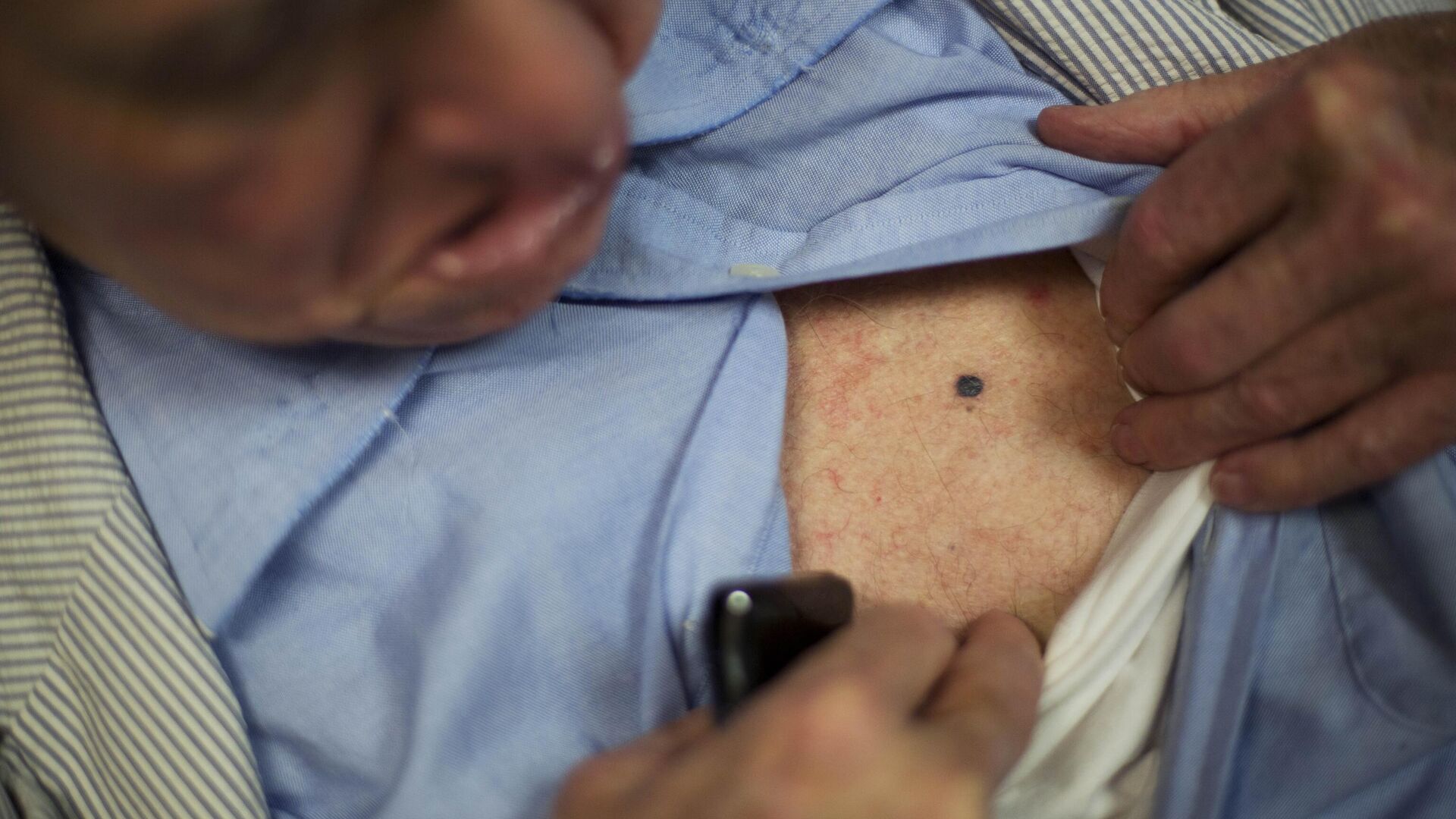
Melanoma is a skin cancer that develops in melanocytes, the cells producing skin pigment. It is particularly dangerous due to its ability to spread... 07.09.2024, Sputnik Africa
2024-09-07T12:43+0200
2024-09-07T12:43+0200
2024-09-10T12:14+0200
sub-saharan africa
zimbabwe
johannesburg
south africa
drugs
medicine
cancer
disease
artificial intelligence (ai)
world health organization (who)
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.africa/img/07e8/09/07/1068184775_0:166:3072:1894_1920x0_80_0_0_a0f7687e541679f0f2b6e169009df52a.jpg
In a major breakthrough for global health, Zimbabwean scientists have announced the discovery of a potential cure for Alzheimer's disease and an advanced treatment for melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer. The revolutionary findings were shared at a press conference in Harare on Thursday by Professor Simon Mukwembi, the lead scientist on the project, media reported.The discovery is powered by a sophisticated computer system called Rutava, which utilizes artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and complex mathematical algorithms to identify chemical compounds that specifically target malignant cancer cells, leaving healthy cells unharmed. Rutava has also been employed to develop a treatment for Alzheimer’s, raising hopes for millions suffering from this neurodegenerative disease.A New Era in Drug DiscoverySpeaking to reporters, Mukwembi described Rutava as a groundbreaking digital technology that significantly accelerates the drug discovery process, reducing the time it takes to develop new treatments from years to mere months. Traditionally, drug development can take over 15 years and billions of dollars for a single compound. With Rutava, however, this timeline is drastically shortened, and the cost is reduced.He added that Rutava’s ability to learn from vast datasets means the system becomes more efficient and accurate each time it is used.Using Rutava, the team has discovered chemical compounds that specifically target and destroy melanoma cancer cells, offering a far more effective treatment than current therapies, which often damage healthy cells as well. The Alzheimer's treatment similarly represents a significant leap forward in combating a disease for which no cure currently exists.Global ImplicationsThe research, conducted in partnership with the University of Witwatersrand and the University of Johannesburg in South Africa, could have profound implications for global healthcare. According to Mukwembi, the application of Rutava in the pharmaceutical industry could position the Global South as a key player in drug discovery and development, enabling it to compete on a global scale.Next Steps: Clinical TrialsWhile the discovery is being hailed as a major advancement, Mukwembi stressed that clinical trials will be necessary to fully validate the effectiveness of these treatments in humans.Dr. Amos Marume, the principal of the Harare Institute of Public Health, and Dr. Isaac Mutingwende, the registrar, were also present at the press conference, reinforcing the significance of the discovery. They noted that while the journey to clinical use may take some time, the initial results are very promising.A Hopeful FutureAlzheimer’s disease affects about 57 million people worldwide, with that number expected to nearly double by 2050, according to a study done by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Meanwhile, melanoma, though not the most common form of cancer, remains highly aggressive, with an estimated 330,000 new cases diagnosed globally in 2022, leading to almost 60,000 deaths, as per the World Health Organization.With millions of lives at stake, the potential of Rutava to revolutionize treatments for cancer and Alzheimer's is immense. If clinical trials prove successful, this breakthrough could not only provide relief to those suffering from these diseases but also transform the global pharmaceutical landscape, making effective treatments more accessible and affordable.
https://en.sputniknews.africa/20240807/south-africa-achieves-breakthrough-in-new-tb-vaccine-what-are-the-benefits-1067761183.html
https://en.sputniknews.africa/20240729/expert-insights-unlocking-secrets-to-preventing-dementia-1067670072.html
zimbabwe
johannesburg
south africa
southern africa
Sputnik Africa
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
2024
Christina Glazkova
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.africa/img/07e7/0b/07/1063380906_0:0:673:674_100x100_80_0_0_79628b4d0cd9f29291a57aa13bbf9e7a.jpg
Christina Glazkova
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.africa/img/07e7/0b/07/1063380906_0:0:673:674_100x100_80_0_0_79628b4d0cd9f29291a57aa13bbf9e7a.jpg
News
en_EN
Sputnik Africa
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Sputnik Africa
feedback@sputniknews.com
+74956456601
MIA „Rossiya Segodnya“
Christina Glazkova
https://cdn1.img.sputniknews.africa/img/07e7/0b/07/1063380906_0:0:673:674_100x100_80_0_0_79628b4d0cd9f29291a57aa13bbf9e7a.jpg
zimbabwe, johannesburg, south africa, drugs, medicine, cancer, disease, artificial intelligence (ai), world health organization (who), southern africa, health, healthcare, science
zimbabwe, johannesburg, south africa, drugs, medicine, cancer, disease, artificial intelligence (ai), world health organization (who), southern africa, health, healthcare, science
Groundbreaking Discovery: Zimbabwean Scientists Announce Cure for Alzheimer's and Melanoma
12:43 07.09.2024 (Updated: 12:14 10.09.2024) Christina Glazkova
Writer / Editor
Melanoma is a skin cancer that develops in melanocytes, the cells producing skin pigment. It is particularly dangerous due to its ability to spread. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder affecting memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the leading cause of dementia, gradually impairing cognitive function and daily life.
In a major breakthrough for global health, Zimbabwean scientists have announced the discovery of a potential cure for
Alzheimer's disease and an advanced treatment for melanoma, a deadly form of skin cancer. The revolutionary findings were shared at a press conference in Harare on Thursday by Professor Simon Mukwembi, the lead scientist on the project, media reported.
The discovery is powered by a sophisticated computer system called Rutava, which utilizes artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and complex mathematical algorithms to identify chemical compounds that specifically target malignant cancer cells, leaving healthy cells unharmed. Rutava has also been employed to develop a treatment for Alzheimer’s, raising hopes for millions suffering from this neurodegenerative
disease.A New Era in Drug Discovery
Speaking to reporters, Mukwembi described Rutava as a groundbreaking digital technology that significantly accelerates the drug discovery process, reducing the time it takes to develop new treatments from years to mere months. Traditionally, drug development can take over 15 years and billions of dollars for a single compound. With Rutava, however, this timeline is drastically shortened, and the cost is reduced.
“The good thing that Rutava does is you can recalibrate it for other diseases. So, for the cancer, we've got quite a number of cancers, right? What we have worked on right now is melanoma skin cancer. But of course, we can extend out to sort out all the other cancers without difficulty because we now have the innovative technology. […] We also developed, using the Rutava, a cure for Alzheimer's disease,” Mukwembi was quoted as saying.
He added that Rutava’s ability to learn from vast datasets means the system becomes more efficient and accurate each time it is used.
Using Rutava, the team has discovered chemical compounds that specifically target and destroy melanoma
cancer cells, offering a far more effective treatment than current therapies, which often damage healthy cells as well. The Alzheimer's treatment similarly represents a significant leap forward in combating a disease for which no cure currently exists.
The research, conducted in partnership with the University of Witwatersrand and the University of Johannesburg in
South Africa, could have profound implications for global healthcare. According to Mukwembi, the application of Rutava in the pharmaceutical industry could position the Global South as a key player in drug discovery and development, enabling it to compete on a global scale.
“Our technology is disruptive in that it greatly makes it much, much possible for the Global South to be able to turn itself into a pharmaceutical giant of the world because it's cheaper in terms of time. The technology will take just a few months to run through just the screening of a molecule, up to formulation studies and clinical trials. So, it does help in all those. Turning 15 years to a year, this shows its disruptive technology in the pharmaceutical value chain,” he said, as cited by media.
Next Steps: Clinical Trials
While the discovery is being hailed as a major advancement, Mukwembi stressed that clinical trials will be necessary to fully validate the effectiveness of these treatments in humans.
Dr. Amos Marume, the principal of the Harare Institute of Public Health, and Dr. Isaac Mutingwende, the registrar, were also present at the press conference, reinforcing the significance of the discovery. They noted that while the journey to clinical use may take some time, the initial results are very promising.
Alzheimer’s disease affects about 57 million people worldwide, with that number expected to nearly double by 2050, according to a
study done by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Meanwhile,
melanoma, though not the most common form of cancer, remains highly aggressive, with an estimated 330,000 new cases diagnosed globally in 2022, leading to almost 60,000 deaths, as per the World Health Organization.
With millions of lives at stake, the potential of Rutava to revolutionize treatments for cancer and Alzheimer's is immense. If clinical trials prove successful, this breakthrough could not only provide relief to those suffering from these diseases but also transform the global pharmaceutical landscape, making effective treatments more accessible and affordable.